Find out how to flush and reset DNS Cache
We show you our simple guide: How to flush and reset the DNS cache.
Often we have to solve internet problems on both Windows and Mac and surprisingly it is often resolved just by running the command below.
What is DNS?
To explain DNS it means Dynamic Name Service,
the idea is DNS is it changes internet addresses such as www.example.com to an IP address such as 192.168.0.1.
As the Internet doesn’t actually know what the word version of an address is.
Once you type an address in your browser the DNS server translates this into an address,
for example, our site www.hgmssp.co.uk translates to 75.119.211.180 which can be seen by using Command Prompt (CMD):
What will clearing the DNS do?
Clearing your DNS cache can help resolve DNS issues.
If you are having issues accessing web pages it may be because the host has changed addresses,
but your computer has stored an old version which will result in errors connecting to the pages.
Recently a client had changed Email providers and they weren’t receiving email,
the cause was due to both the local computers and their server retaining the former IP (Internet Protocol) address.
Flushing the DNS cache was a solution that prevented a large financial loss due to potentially not receiving any mail orders.
How to flush and reset your DNS Cache
So now you understand a little bit about what DNS is, to actually flush your cache you can access it from two places in Windows:
Method 1:
Go to: Run by pressing the Windows Key (flag) + R and typing in ipconfig /flushdns as shown below:
Method 2:
The second way is the more traditional way. Access Command Prompt,
in Windows 10 right-click the start menu and select Command Prompt (admin) and from here type ipconfig /flushdns the result can be seen below:
How to Flush and Reset DNS Cache on Mac
With MacOSX the way you reset the cache has changed over the versions please see the details below:
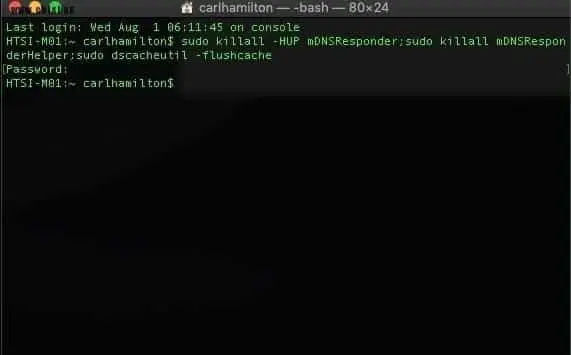
Sierra and later
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;sudo killall mDNSResponderHelper;sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
El Capitan
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Yosemite
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Older Versions
dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder






